How Ankle Arthroscopy Works: A Comprehensive Guide
Ankle arthroscopy is an advanced surgical technique that offers patients an effective solution to a variety of ankle joint issues. From diagnosing and treating ankle arthritis to repairing tendon damage, this minimally invasive procedure is a game-changer in the world of orthopedic surgery.
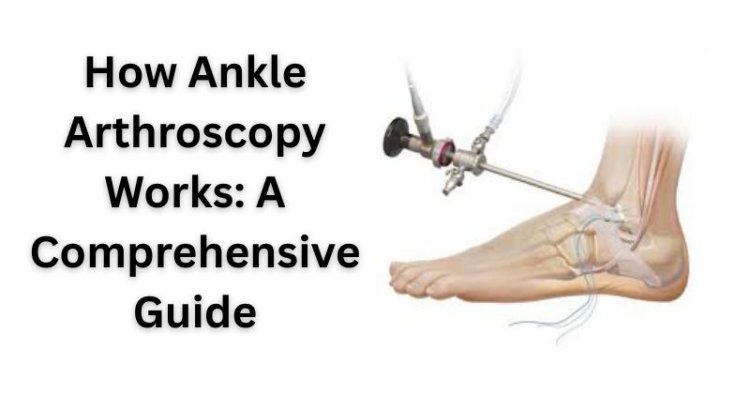
Ankle injuries are common among active individuals and athletes, often leading to chronic pain, limited mobility, and the need for surgical intervention. One of the most advanced techniques used to treat these injuries is ankle arthroscopy. This minimally invasive procedure has revolutionized the way ankle conditions are treated, offering patients quicker recovery times, less pain, and smaller scars. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore how ankle arthroscopy works, the conditions it treats, and what patients can expect from the procedure.
What is Ankle Arthroscopy?
Ankle arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat a variety of ankle joint issues. The procedure involves inserting a small camera, called an arthroscope, into the ankle joint through tiny incisions. The camera sends real-time images to a monitor, allowing the surgeon to see the inside of the joint and perform surgical repairs or remove damaged tissue.
Because ankle arthroscopy uses small incisions and specialized instruments, it typically causes less trauma to the surrounding tissues compared to traditional open surgery. This means that patients often experience less pain, a faster recovery, and a reduced risk of complications.
When is Ankle Arthroscopy Surgery Recommended?
Ankle arthroscopy surgery is commonly used to treat a range of conditions that affect the ankle joint, including:
1. Ankle Arthritis
Chronic wear and tear or injury can lead to arthritis in the ankle joint. In cases where conservative treatments (like physical therapy, medications, or injections) don't provide relief, ankle arthroscopy surgery can be used to remove damaged tissue, smooth rough surfaces, or even remove bone spurs, helping to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
2. Ankle Fractures
Sometimes, fractures or broken bones in the ankle joint require surgical intervention. Ankle arthroscopy can be used to access the injured area, clean up any debris, and inspect the joint for further damage. This can ensure that the ankle heals properly, reducing the likelihood of future complications.
3. Chronic Ankle Instability
For individuals who suffer from recurrent ankle sprains or instability, ankle arthroscopy can help by examining the ligaments and other soft tissues. It can be used to repair or tighten ligaments, providing greater stability and reducing the risk of future sprains.
4. Tendon Issues
Tendons around the ankle joint can become inflamed or damaged due to overuse or injury. Ankle arthroscopy surgery can be used to remove damaged tissue, relieve pressure, or even address conditions like tendon tears or tendinitis.
5. Synovitis
Synovitis refers to inflammation of the synovial lining in the joint. This condition can be painful and lead to swelling. Through ankle arthroscopy, the surgeon can remove the inflamed tissue, reducing discomfort and inflammation.
How Does Ankle Arthroscopy Work?
Preparation for the Procedure
Before the procedure, the surgeon will conduct a thorough evaluation of the patient's condition. This often involves a physical exam, medical history review, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs to get a clearer picture of the joint's state.
The patient is typically placed under general anesthesia or regional anesthesia, depending on the complexity of the procedure and the patient's preferences.
Step-by-Step Process of Ankle Arthroscopy
-
Incision and Insertion of the Arthroscope
The surgeon makes a small incision, usually about 1 cm, near the ankle joint. The arthroscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera) is then inserted through this incision. The camera provides real-time images of the joint, which are displayed on a monitor.
-
Inspection and Diagnosis
Once inside the joint, the surgeon can inspect the soft tissues, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. This allows for a thorough diagnosis of any damage or abnormalities.
-
Treatment
If treatment is necessary, the surgeon can use specialized instruments, also inserted through tiny incisions, to remove damaged tissue, smooth rough cartilage, or repair torn ligaments. In some cases, the surgeon may use the arthroscope to guide the placement of sutures or other repair materials.
-
Closure and Post-Surgery Care
After the procedure is completed, the incisions are closed using stitches or adhesive strips. The patient is then moved to a recovery area, where they are monitored as the anesthesia wears off.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
One of the primary advantages of ankle arthroscopy surgery is the relatively quick recovery time compared to traditional open surgeries. While every patient is different, most people can expect to resume normal activities within 6 to 12 weeks after surgery.
Immediately following the procedure, the patient may need to wear a brace or splint to protect the ankle and reduce swelling. Ice and elevation are commonly recommended to manage pain and swelling during the first few days. Physical therapy is often recommended to restore strength and mobility, particularly if the surgery involved repairing ligaments or tendons.
Risks and Considerations
Like any surgery, ankle arthroscopy surgery does come with some risks, although they are generally low. Potential complications include:
-
Infection at the incision site
-
Nerve or blood vessel injury
-
Blood clots
-
Scar tissue formation that can affect joint mobility
However, when performed by a skilled surgeon, ankle arthroscopy is considered to be a safe and effective procedure with a high success rate.
Benefits of Ankle Arthroscopy
-
Minimally invasive: Smaller incisions lead to less tissue damage and scarring.
-
Faster recovery: Many patients can return to regular activities within a few weeks.
-
Less pain: Because the procedure is minimally invasive, patients typically experience less post-operative pain compared to open surgery.
-
Reduced risk of complications: Smaller incisions reduce the risk of infection, blood loss, and other complications associated with traditional surgery.
Conclusion
Ankle arthroscopy is an advanced surgical technique that offers patients an effective solution to a variety of ankle joint issues. From diagnosing and treating ankle arthritis to repairing tendon damage, this minimally invasive procedure is a game-changer in the world of orthopedic surgery. If you're experiencing ankle pain or discomfort that hasn't responded to conservative treatments, ankle arthroscopy surgery may be the right option for you. Always consult with a qualified orthopedic surgeon to discuss your condition and explore the best treatment options.
for more(click here)
What's Your Reaction?














